Stem cell therapy research is the key to developing cures for degenerative conditions like Parkinson’s and motor neuron disease from which I and many others suffer. The fact that the cells may come from embryos is not an objection, because the embryos are going to die anyway.
–STEPHEN HAWKING
Video credit: Cell Health Institute
What is a Stem Cell?
Stem cells are special human cells that are able to develop into many different cell types. In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. Stem cells are the body’s raw materials — cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated. Under the right conditions in the body or a laboratory, stem cells divide to form more cells called daughter cells.
These daughter cells either become new stem cells (self-renewal) or become specialized cells (differentiation) with a more specific function, such as blood cells, brain cells, heart muscle cells or bone cells. All stem cells can self-renew (make copies of themselves) and differentiate (develop into more specialized cells). Beyond these two critical abilities, though, stem cells vary widely in what they can and cannot do and in the circumstances under which they can and cannot do certain things.
Types of Stem Cell
Embryonic Stem Cells
Image Credit: PIXABAY
Embryonic stem cells are obtained from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst, a mainly hollow ball of cells that, in the human, forms three to five days after an egg cell is fertilized by a sperm. This involves fertilizing an embryo inside a laboratory instead of inside a female body. Most of the embryonic stem cells that are used in stem cell therapy research today are derived from unused embryos that have been fertilized through an in vitro fertilization process that was performed at a medical clinic. Then they are donated, with informed consent, by donors for research and medicinal purposes.
Adult Stem Cells
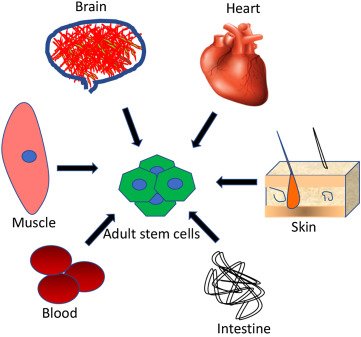
Image Credit: ScienceDirect
Found in bone marrow and peripheral blood have the ability to change into other types of cells as well. However, they are difficult to acquire, the cells are the same age as the donor is and there is an increased risk of rejection by the recipient. One type comes from fully developed tissues such as the brain, skin, and bone marrow. There are only small numbers of stem cells in these tissues. They are more likely to generate only certain types of cells. For example, a stem cell that comes from the liver will only make more liver cells.
Adult stem cells are said to be multipotent, which means they can only change into some cells in the body, not any cell, for example:
Blood (or ‘haematopoietic’) stem cells can only replace the various types of cells in the blood.
1: Skin (or ‘epithelial’) stem cells provide the different types of cells that make up our skin and hair.
2: Blood (or ‘haematopoietic’) stem cells can only replace the various types of cells in the blood.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
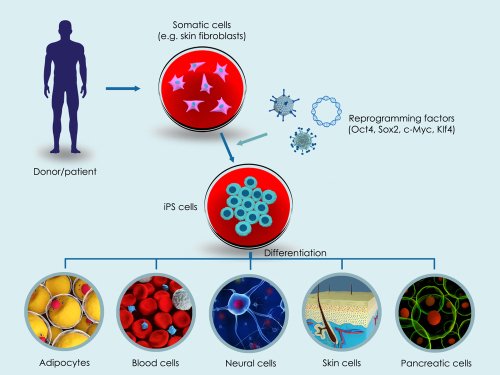
Image Credit: GenScript
Induced means that they are made in the lab by taking normal adult cells, like skin or blood cells, and reprogramming them to become stem cells.
Cord Blood Stem Cells
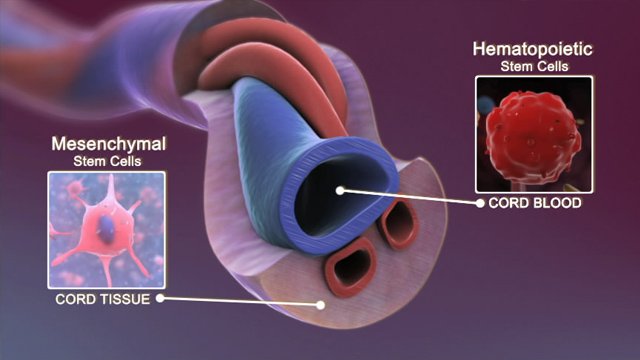
Image Credit: Unmass Medical School
Cord blood stem cells are younger than adult stem cells and have tremendous abilities to change into different types of cells and to continually divide and renew themselves. Because of this, there are fewer incidences of Graft Versus Host Disease (GVHD), where the body rejects the transfused stem cells. Another very important point about cord blood stem cells is that, unlike embryonic stem cells, cord blood stem cells are free of ethical debate because these cells if not used would just be thrown away.
Fetal Stem Cells
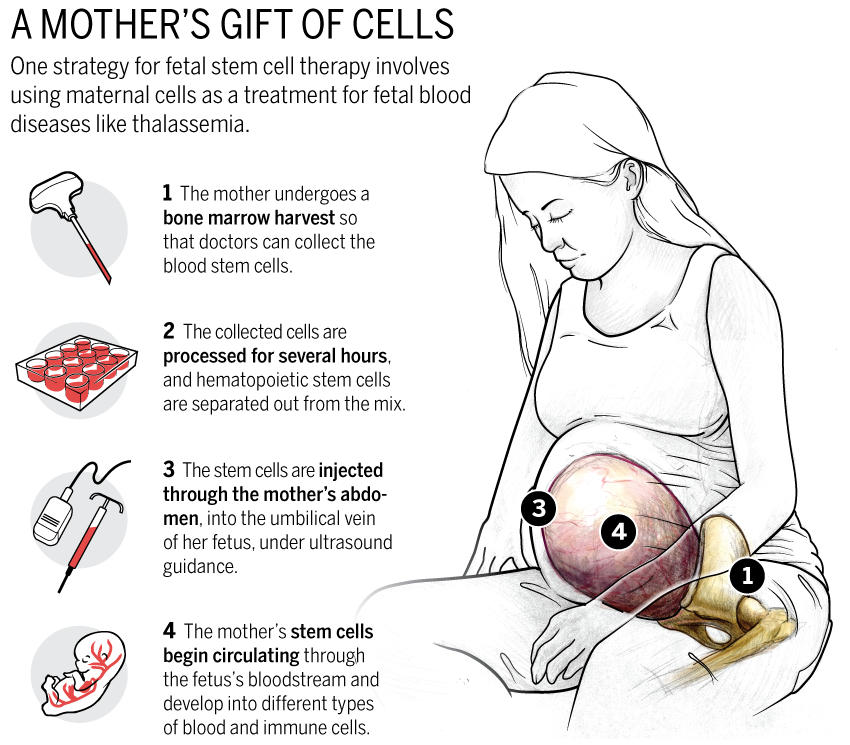
Image Credit: ScienceMag
Today, many expectant mothers are asked to store some of their umbilical cord blood, which is typically discarded. However, umbilical cord blood contains embryonic stem cells that can be grown in a culture. These types of stem cells are multipotent. Unlike stem cells that were harvested at an earlier age in development, fetal stem cells can only differentiate into a limited number of cells.Umbilical cord blood also contains haematopoietic stem cells, similar to those found in bone marrow, and can be used to regenerate red blood cells and cells of the immune system.
Mesenchymal stem cells
Image Credit: BioInformant
MSCs come from the connective tissue or stroma that surrounds the body’s organs and other tissues. Scientists have used MSCs to create new body tissues, such as bone, cartilage, and fat cells. They may one day play a role in solving a wide range of health problems. The first MSCs were discovered in the bone marrow and were shown to be capable of making bone, cartilage and fat cells. Since then, they have been grown from other tissues, such as fat and cord blood. Various MSCs are thought to have stem cell, and even immunomodulatory, properties and are being tested as treatments for a great many disorders, but there is little evidence to date that they are beneficial. Scientists do not fully understand whether these cells are actually stem cells or what types of cells they are capable of generating. They do agree that not all MSCs are the same, and that their characteristics depend on where in the body they come from and how they are isolated and grown.
Stem Cell Therapy for the Knee
Osteoarthritis is a chronic degenerative disorder that ultimately leads to a gradual deterioration of knee joint cartilage and also may be the result of a prior injury to the knee joint such as a fracture, tendon damage and ligament tears.This may lead to joint instability which can cause wear and tear to the articular cartilage. Arthritis can affect not only the cartilage but may lead to damage of the bone beneath the cartilage, the synovial lining to the joint, ligaments, tendons, and muscles.
Stem cell therapy for knees involves extracting stem cells from bone marrow or fat and then injecting them into the knee using image guidance. The procedure is minimally invasive and is believed to work by decreasing inflammation, healing damage by developing into new cartilage, and releasing cytokines, which are proteins that reduce pain and slow degeneration of the remaining cartilage.
Injection of progenitor cells, especially mesenchymal stem cells, has been shown to be a better strategy to repair degenerative cartilage than implantation of differentiated cells such as articular cartilage. Adult stem cells have a reliable potential to differentiate into cartilage, bone, fat or soft tissue.
Video Credit: Regenomics
They also display the ability to home to areas of inflammation and degeneration, and to modify immune system activity that can favorably influence the surrounding cartilage in areas of damage.
Encouragingly, results of pre-clinical and clinical trials have provided initial evidence of efficacy and safety in the therapeutic use of mesenchymal stem cell therapies for the treatment of knee cartilage damage and osteoarthritis. Cell-based therapy has become a key focus of tissue engineering research focused on functional replacement of cartilage and meniscus regeneration.
Platelet-rich plasma, or PRP, is also a form of regenerative medicine and involves injecting a concentration of your own platelets into the knees in order to accelerate healing of the damaged areas. Platelets play a vital role in helping the body repair itself, and after they are injected into the affected area, they release growth factors that increase the number of reparative cells. There are very few side effects associated with the procedure, and like arthritis stem cell therapy, it is minimally invasive. Other types of treatments for chronic knee pain involve injecting corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid into the knees and various types of surgery, such as partial or total knee replacement.
Stem Cell Extraction Methods
- Collecting Blood: The largest concentration of blood stem cells is in your bone marrow. However, the blood stem cells can be moved or “mobilized” out of the bone marrow into the bloodstream (peripheral blood) where they can be easily collected. Most transplants these days use stem cells collected from the bloodstream.
When blood stem cells are collected from the bloodstream, the procedure is called a peripheral blood stem cell collection or harvest.
- Collecting Bone Marrow: The procedure used to collect bone marrow for transplant is called a bone marrow harvest. It is a surgical procedure that takes place in a hospital operating room. Typically it is done as an outpatient procedure.
Video Credit: Hemaquebec1998
The amount of bone marrow harvested depends on the size of the patient and the concentration of blood stem cells in your marrow.
- Collecting Fat: Fat derived stem cells show an enhanced ability to differentiate into cartilage and are found in dramatically higher numbers than seen in bone marrow. Not only are they typically 500-2000 times more abundant but they don’t decrease as we age. Fat derived cells have been shown to be successfully employed to target cartilage defects and improve osteoarthritis in patient studies. Fat derived adult stem cells have also demonstrated improved outcomes over bone marrow for cartilage repair.
Can Stem Therapy cure Diabetes and Cancer?
Understanding the root causes of diabetes has eluded researchers for many years now.The way in which the immune system causes the destruction of precious beta islet cells within the pancreas of type 1 diabetics is generally understood to be the key. The ultimate goal, which has so far proved elusive, is a cure for diabetes, which could potentially be available for both types of diabetes through stem cell research
3 Types of Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1 diabetes: This results from your body’s failure to generate insulin, and currently requires the individual to inject insulin. (Likewise known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, IDDM for short, and juvenile diabetes)- Cell therapy to stop immune cells from destroying insulin-producing pancreatic islet cells. The usual symptoms that are associated with Type 1 diabetes can include Polydipsia (constant thirst), polyuria (excessive urination), polyphagia (constant hunger), weight loss, dry mouth and fatigue. A diagnosis of Type 1 results in the destruction of beta cells in the patient’s pancreas. Other known complications for type 1 diabetes include heart disease, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic neuropathy and kidney disease. Type 1 diabetes is especially dangerous for women who have a 42% higher risk of mortality as compared to men. The average life expectancy for type 1 diabetics is less than 11 years for men and less than 13 years for females.
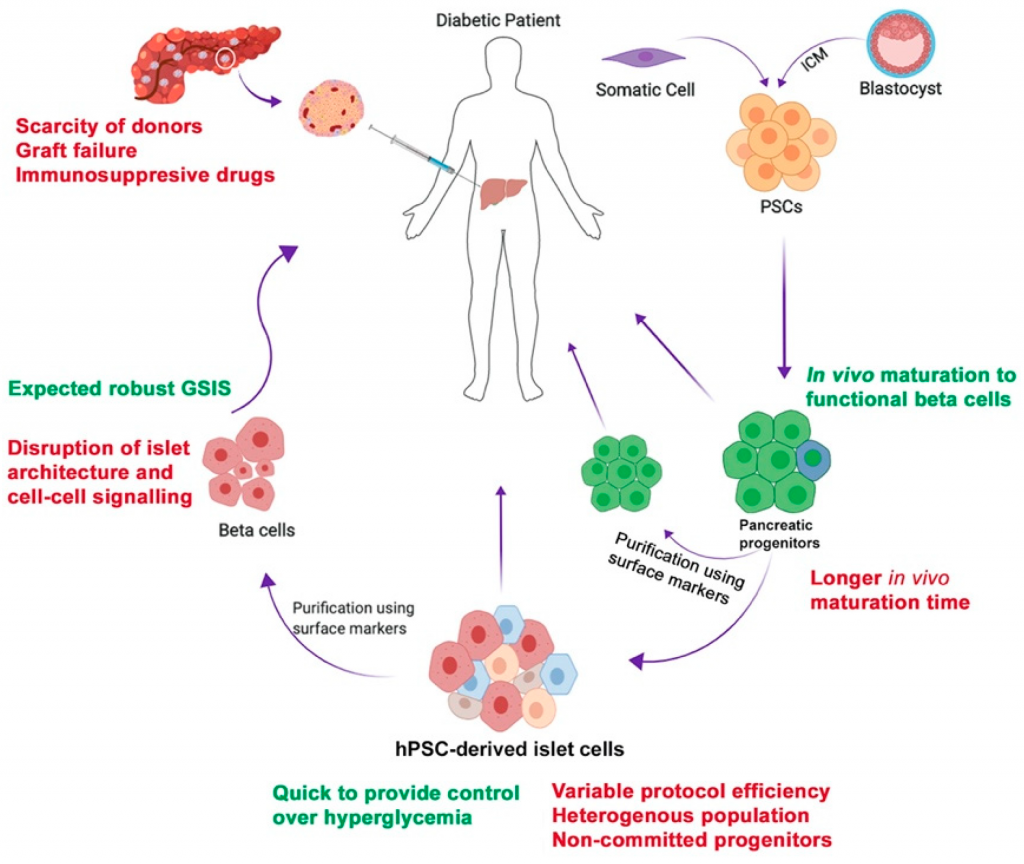
Image Credit: MDPI
Type 2 diabetes: results from insulin resistance, a condition wherein cells are not able to use insulin appropriately, sometimes coupled with a complete insulin deficiency. – Type 2 is often an acquired disease and if caught early is a very treatable condition at the regeneration center. Long-term risks of having diabetes include retinopathy (loss of vision), diabetic nephropathy which leads to kidney failure, peripheral neuropathy ( foot ulcers that lead to amputations or Charcot joints ), and autonomic neuropathy that causes genito-urinary, gastro-intestinal, cardio vascular symptoms with sexual dysfunction. Patients diagnosed with diabetes also report increased occurrences of peripheral arterial disease (PAD), atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and cerebrovascular disease. Other complications include Hypertension and severe abnormalities of lipoprotein metabolism. Many patients can also impair insulin secretion because of pharmaceutical medications they are taking. These medications do not directly cause diabetes, but they may lead individuals to become insulin resistant.
Gestational Diabetes is when pregnant women, who’ve never had diabetes before, have a high blood glucose level while being pregnant. It may precede the development of type 2 DM.
Currently there is no treatment to Gestational diabetes with stem cell therapy.
Stem Cells for Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes is characterized by the body’s inability to produce insulin and therefore necessitates daily injections of insulin. Because it most often develops in children, it is often referred to as “juvenile diabetes.” The Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation (JDRF) reports that as many as three million Americans may have type 1 diabetes (T1D) and an average of 40 children each day (more than 15,000 per year) are diagnosed. Stabilizing insulin levels is the key to managing diabetes. The standard treatment today focusses on supplementing the body’s insulin, typically through injection (needles) or insulin pumps, which are worn outside the body. This requires the patient testing his or her blood sugar levels several times per day and carefully maintaining blood insulin levels. While this is recognized as the best standard of care currently, researchers hope to find a way to help the body produce or better regulate its own insulin levels.
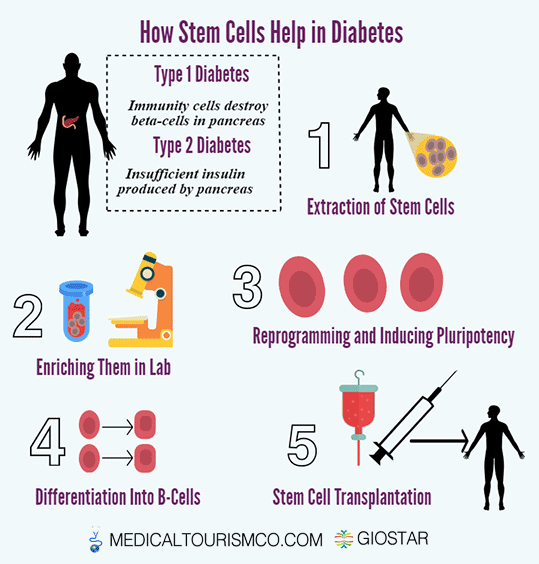
Image Credit: Medical tourism Corporation
Stem Cells for type 2 Diabetes
At this stage, cures for Type 1 diabetes or gestational diabetes are very very low probability. There is a genetic component of the disease that will require gene therapy to reprogram the cells from reverting back to their compromised states however these solutions are just in the clinical trials stage and have not been approved for clinical applications. Type 2 Diabetes T2D however is usually treatable and reversible if caught early enough before it starts affecting other organs/systems in the body. Often time, patients simply ignore the disease and try to manage the symptoms using traditional diabetes medication (Metformin, Thiazolidinediones, DPP-4 inhibitors, Meglitinides), change of diet and/or regular insulin therapy. If metabolic diseases are left untreated, complications often occur and can include:
- Foot Complications / Ulcers
- Kidney Disease (Nephropathy) and PKD
- Ketones & DKA (Ketoacidosis)
- Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease – IBD
- High Blood Pressure & Hypertension ( leads to heart disease, eye problems )
- Gastroparesis
- HHNS – Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome
- Pancreas Cancer
- Brain Strokes
Please note patients with severe or multiple conditions may have travel restrictions and unable to travel to Thailand. All potential candidates seeking stem cells for diabetes must be approved in advance using current/actual medical records and results from recent blood panels including HbA1C, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), Blood pressure and Lipid profiles.
Stem Cell Transplants in Cancer Treatment
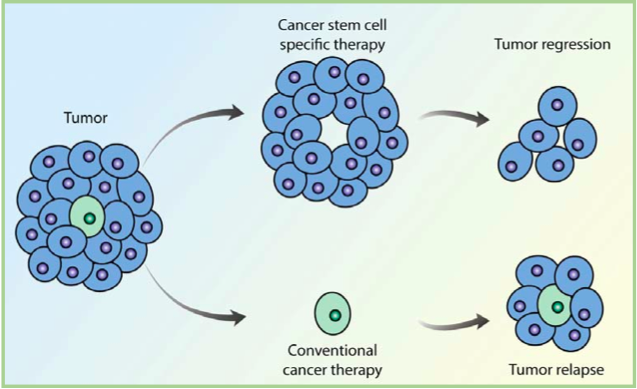
Image Credit: Harvard Stem Cell Institute
Stem cell transplants are procedures that restore blood-forming stem cells in people who have had theirs destroyed by the very high doses of chemotherapy or radiation therapy that are used to treat certain cancers. In these conditions, patients need to receive the intravenous infusion of autologous or allogeneic HSCs. These HSCs are supposed to exert a homing process that leads to their rapid migration into defined stem cell niches in bone marrow (BM). After encountering BM, the transplanted HSCs undergo the en-graftment process prior to giving rise to specialized blood cells.
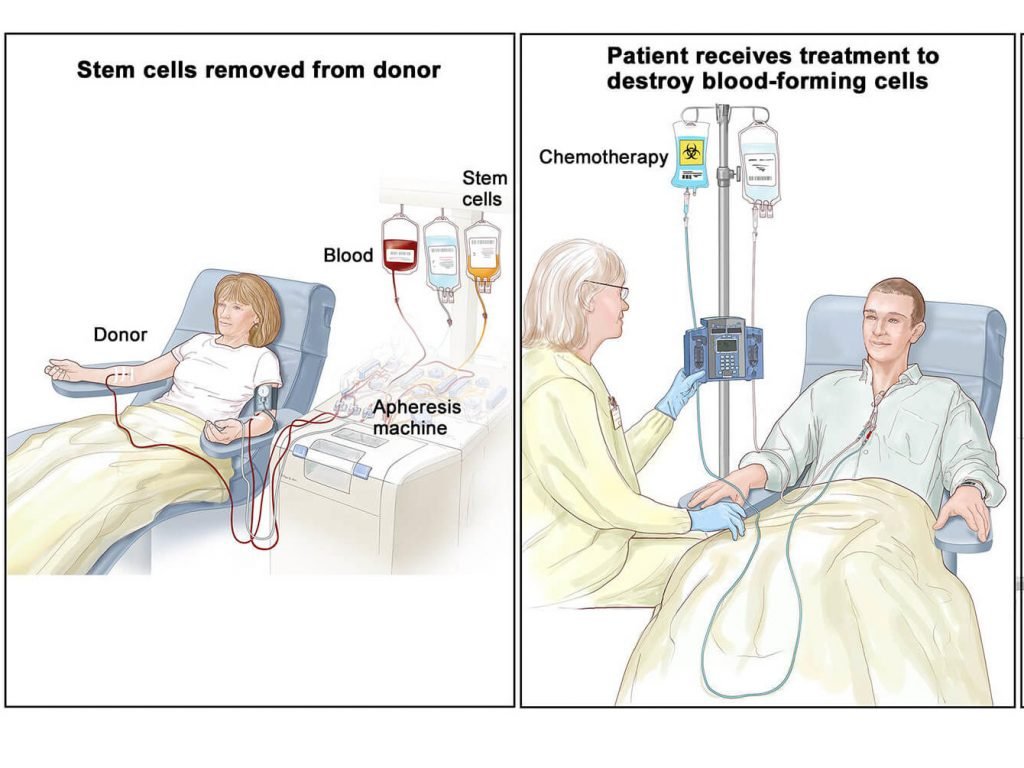
Image Credit: National Cancer Institute
Conclusion
Stem Cell therapy in a glance:

Image Credit: MsTrust
Patients who undergo SVF stem cell therapy for knee joint arthritis report a reduction in their painful symptoms and an increase in range of motion and mobility. Stem cell therapy helps to quickly reduce knee joint inflammation, and many patients see improvements in just 1 to 2 days. Anti-inflammatory results of the procedure lasts 2 to 3 months and many patients see a gradual improvement in their overall condition over time
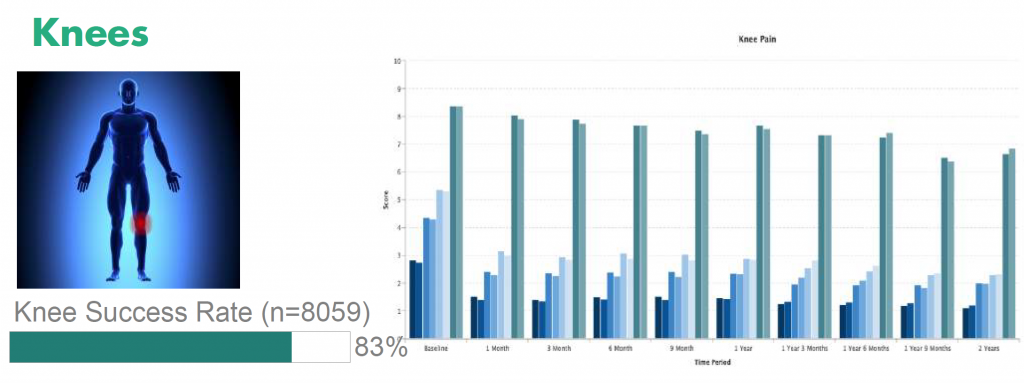
Image Credit: InnovationsMedical
Patient feedback on stem cell therapy
“I was having terrible knee pain all the time and it was difficult to just walk and use the stairs. I was referred to Dr. Brandt and Thrive MD by a friend. I had my consultation and found out that I would be a great candidate for stem cell therapy. I had my procedure on Nov 22, 2017 and within two weeks my pain which on a scale of 1-10, was 7-8 all the time went to 0-1. I’m now 3 months post procedure and I have 0 knee pain.”
Video Credit: ThriveMD
Frank’s cancer is now in remission and he’s been able to go back to work. He doesn’t know if the pills helped but he’s proud of being a stem cell pioneer and hopes the first-in-human therapy proves effective so that one day many others will be as lucky as he is.
Video Credit: California Institute of Regenerative Medicine
Hope you get an insight into the medical advancements taking place around the globe and how easy it is becoming to combat deadliest diseases with such advancements.Continuous research has come up with less painful and fruitful solutions in medical science.